💡 Chain Abstraction is in early access.
How It Works
Apps need to pass
gas as null, while sending a transaction to allow proper gas estimation by the wallet. Refer to this guide for more details.- Check if the required chain has enough funds to complete the transaction
- If not, use the
preparemethod to generate necessary bridging transactions - Sign routing and initial transaction hashes, prepared by the prepare method
- Use
executemethod to broadcast routing and initial transactions and wait for it to be completed
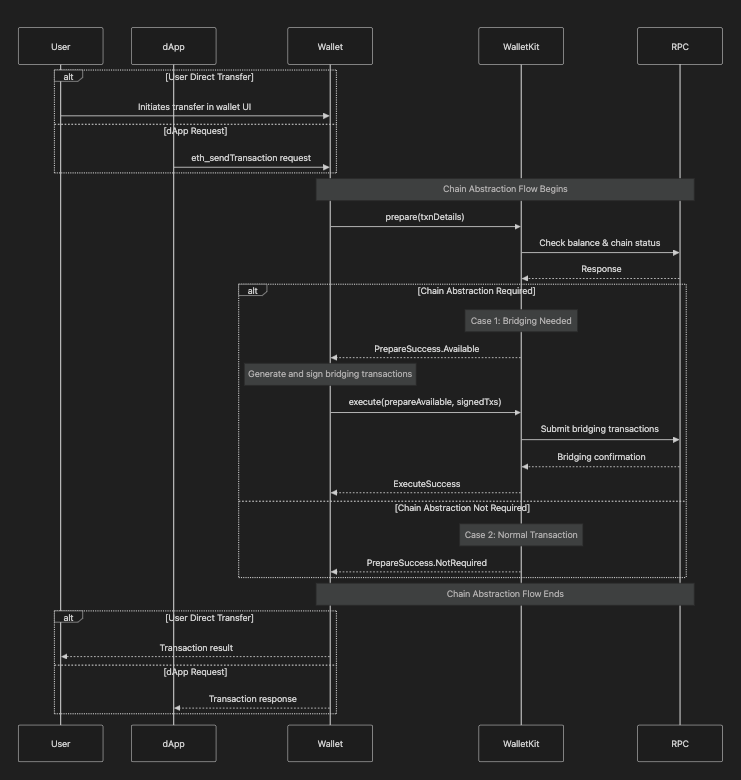
Chain Abstraction Flow
Methods
The following methods from WalletKit are used in implementing chain abstraction.💡 Chain abstraction is currently in the early access phase.Make sure you are using canary version of
@reown/walletkit and @walletconnect/react-native-compatPrepare
This method checks if a transaction requires additional bridging transactions beforehand.Execute
Helper method used to broadcast the bridging and initial transactions and wait for them to be completed.Usage
When sending a transaction, first check if chain abstraction is needed using theprepare method.
If it is needed, you must sign all the fulfillment transactions and use the execute method.
Here’s a complete example:
Error Handling
When implementing Chain Abstraction, you may encounter different types of errors. Here’s how to handle them effectively:Application-Level Errors
These errors (PrepareError) indicate specific issues that need to be addressed and typically require user action:
- Insufficient Gas Fees: User needs to add more gas tokens to their wallet
- Malformed Transaction Requests: Transaction parameters are invalid or incomplete
- Minimum Bridging Amount Not Met: Currently set at $0.60
- Invalid Token or Network Selection: Selected token or network is not supported
Retryable Errors
These errors (Result::Err) indicate temporary issues that may be resolved by retrying the operation.
Examples of these types of issues include network connection timeouts, TLS negotiation issues, service outages, or other transient errors.
For retryable errors, show a generic “oops” message to users and provide a retry button. Log detailed error information to your error tracking service, but avoid displaying technical details to end users.
For errors in the
execute() method, a retry may not resolve the issue. In such cases, allow users to cancel the transaction, return them to the application, and let the application initiate a new transaction.